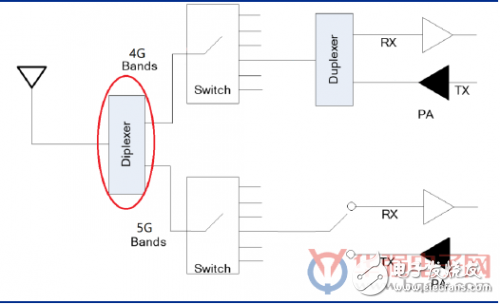
In June of this year, 3GPP announced that the 5G independent networking (SA) standard was officially frozen. Whether my country's 5G construction adopts the latest frozen SA architecture or the non-independent networking (NSA) architecture that was frozen as early as December 2017, arousing heated discussions in the market. The 5G network architecture includes independent SA and NSA combined with 4G network: Independent networking mode (SA): Refers to a new 5G network, including new base stations, backhaul links, and core networks. While SA has introduced new network elements and interfaces, it will also adopt new technologies such as network virtualization and software-defined networking on a large scale, and combine them with 5GNR. At the same time, the technical challenges faced by its protocol development, network planning and deployment, and interoperability will be Beyond 3G and 4G systems. Non-independent networking mode (NSA): Non-independent networking refers to the deployment of 5G networks using the existing 4G infrastructure. The 5G carrier based on the NSA architecture only carries user data, and its control signaling is still transmitted through the 4G network. Operators can determine upgrade sites and areas based on business requirements, and complete contiguous coverage is not necessarily required. Recently, whether the domestic 5G network will adopt the independent networking mode (SA) or the non-independent networking mode (NSA) has triggered heated discussions in the market. 1.1. What are the advantages of NSA? The SA architecture is simpler in comparison, while the NSA architecture is slightly more complicated. Compared with SA, NSA's main advantages include: 1) Expand 5G coverage with the current mature 4G network. Due to the limited transmission power of mobile phone terminals, the coverage of 5G network is mainly limited by the uplink (that is, the mobile phone sends signals to the base station), so the coverage of 5G single station can be expanded through the joint networking with 4G (NSA); 2) The NSA standard ends earlier and the product is more mature. NSA is much earlier than SA standards, and product roadmaps are correspondingly mature earlier. At present, my country's 5G promotion team has basically completed most of the NSA test work; 3) No need to build a new core network. Under the NSA networking, 5G base stations will use the existing 4G core network, eliminating the need for the construction of 5G core networks. 1.2. Compared with SA, the NSA architecture also has the following disadvantages 1) The 4G live network must still be modified. As mentioned above, NSA is a networking method that integrates 4G and 5G networks, so it will inevitably involve the upgrading and transformation of 4G existing networks (including wireless and core networks); at the same time, the 5G NR application frequency band is higher, and the coverage area is smaller. There are 4G network density that cannot meet 5G coverage. 2) Unable to adjust the supplier structure of existing equipment. In the NSA networking mode, it is more dependent on the original equipment investment. The use of NSA requires the uniformity of interoperability, and the equipment of the original network manufacturer still needs to be purchased. Therefore, the operator cannot re-divide the investment structure of the equipment manufacturer. 3) The existing network cannot meet the 5G high reliability and low latency requirements. Since NSA does not need to build a new 5G core network, and NSA needs to use 4G wireless air interface (NSA wireless anchor point is 4G), but the existing 4G core network architecture and 4G air interface cannot meet the 5G requirements for delay and transmission reliability. 1.3. The NSA architecture is helpful for rapid network construction, but it has higher capital expenditure than SA direct network construction Under the premise of continuous coverage, the number of 5G base stations required for dense urban areas with SA or NSA is the same. Taking into account that the domestic 4G network in dense urban areas is within 300 meters, through the analysis of the link budget of 5G base stations in the outdoor scenes of dense urban areas, we believe that the SA network architecture is based on the co-location of 4G/5G base stations. The solution can achieve continuous 5G coverage (under the NSA architecture, 5G and 4G base stations are also required to be co-located); The single station price of SA base station is more advantageous. As NSA requires the same manufacturer of 5G and 4G, SA does not have this requirement. Therefore, under the NSA architecture, the bargaining power of operators when purchasing 5G base stations is bound to weaken. If the domestic 5G commercial license is issued in advance, NSA may become the early network construction choice of some operators, but it will eventually move towards the SA architecture. On the one hand, NSA provides operators with practical options for rapid network construction (more mature products, no need to modify the core network, etc.), but because the 5G 3GPP R16 version supporting enhanced URLLC will be frozen in December 2019, we believe that operators will be in the future If R16 is to be supported, then operators will gradually choose SA architecture for networking in order to achieve commercial support of 5G networks for new low-latency and high-reliability applications such as autonomous driving, industrial interconnection, and telemedicine. Based on the above realistic conditions, we assume: 1) Compared with the SA architecture 5G base station, the single station price of the NSA architecture network construction scheme will be 30%-50% more expensive, plus the 4G station reconstruction cost, it is expected to be under the same scale , The investment of the NSA structure will be 60% -80% more expensive than the SA structure; 2) Taking into account the country’s higher 5G network construction requirements, if operators choose the NSA architecture at the beginning of the network construction in 2019, it is estimated that about 30% of the total 5G construction scale (2019-2020) will be completed before the SA architecture is introduced. The remaining 70% of the construction volume will choose the SA architecture. Compared with the direct use of SA, the total investment scale of 5G wireless network construction is expected to increase by 18% to 24%. (That is: 0.3 × (1.6 ~ 1.8) + 0.7 = (1.18 ~ 1.24)). in conclusion: 1) Choosing the NSA architecture can help operators achieve faster 5G network construction in the early stage, but in the later stage, in order to achieve continuous coverage and support all 5G scenarios, the future evolution to SA is imperative; 2) Compared with the direct use of SA to build the network, the method of using NSA first and then SA to build the network is faster but the total capital expenditure will also increase by about 18%-24%. Based on market debates, we believe that no matter what network architecture domestic operators ultimately adopt, the pace of 5G commercialization will not slow down, and the scale of construction and investment will not shrink. The next step in domestic work will focus on the division of 5G spectrum in order to achieve pre-commercial use within this year. In 2019, with the maturity of terminal chips and the introduction of terminal categories, domestic 5G will be fully commercialized in 2020. First of all, the commercialization of 5G in 2020 is an important part of the "Made in China 2025" blueprint. 5G is not only an enhancement of mobile communication technology, but also an era of interconnection of all things. It also includes the application scenarios of mMTC (large-scale Internet of Things) and URLLC (low-latency communication). 5G network will be the foundation of industrial Internet, Internet of Things, artificial intelligence and other fields. Secondly, China is becoming stronger and stronger, and it will definitely make full use of its industrial scale advantages. The number of participating companies in China’s telecommunications industry chain is increasing, from a few core equipment vendors to dozens of companies now from operators to terminals; Chinese companies’ voice in the formulation of 3GPP standards is no longer comparable to that of 4G. In the follow-up standard meeting, we will make full use of the advantages of industrial scale to strive for benefits, and will not give up the opportunity to exert influence because of the impact of the trade war. According to our speculation, after the freezing of the first standard of 5GNR this time, the advancing speed of the industry chain will be greatly improved. 1. Main equipment vendors: It is estimated that it will take about 6 to 9 months for Huawei and ZTE from the freezing of standards to the release of trial commercial equipment, that is, Q1 to Q2 next year. Huawei and ZTE will be realized sooner as the first echelon of Chinese manufacturers, and it is predicted that Ericsson and Nokia will be later than Chinese manufacturers. 2. Terminal manufacturers: The upstream chip manufacturer's R&D cycle will also take 9 months, and it is expected to be mature in Q2~Q3 next year. Chip products need to be tested for interoperability with equipment. Terminal companies need a period of time to debug after chip products are in hand, and it is expected that mass production of smart phones will not be until Q4 next year to the first half of 2020. 3. CPE products (customer premises equipment): It may appear in Q3 next year, but the penetration rate in China is not high. The general public mainly accepts smart phone equipment 3.1 Features of 5G terminals under NSA architecture: Simultaneous processing of 4G and 5G network data Unlike the 5G terminal under the SA architecture that only needs to process data from the 5G network, the 5G terminal under the NSA architecture needs to process data from the 4G network and the 5G network at the same time. Therefore, supporting the NSA architecture is bound to be more complicated for the design of the 5G terminal. What are the challenges in the design of terminals that support the NSA architecture 5G network? 3.2 Advantages of 5G terminals under NSA architecture: early maturity and high downlink rate First, let's talk about the advantages of 5G terminals under the NSA architecture compared with the SA architecture: 1) Because the NSA standard was frozen earlier, chips supporting the NSA architecture will also be born earlier, and terminals such as mobile phones that support the NSA architecture are also expected to be commercialized earlier; 2) Because the terminal under the NSA architecture needs to connect to 4G and 5G networks at the same time, compared with SA, NSA can superimpose the rate of 4G network, so it will have more advantages in downlink (base station to terminal) rate. 3.3 Challenges of 5G terminals under the NSA architecture: more complex designs, higher device costs, and affected RF performance But at the same time, because 5G terminals need to access 4G networks at the same time under the NSA architecture, they need to support dual connectivity of 4G and 5G networks, which is bound to bring new challenges to 5G terminals: 1) As there are many commercial frequency bands for 4G (take China as an example, 4G frequency bands include 800MHz, 900MHz, 1.8GHz, 1.9GHz, 2.1GHz, 2.3GHz, 2. 6GHz and other frequency bands), so unless they are used Customization (that is, only supports a specific 4G frequency band), otherwise, in order to take into account different 4G frequency bands at the same time, the design of the radio frequency of the terminal that supports dual connections will be very complicated; 2) In order to meet the two-way signal connection of the terminal at the same time, it is necessary to introduce the component of the duplexer (as shown in the red circle in the above figure), so it will inevitably bring about an increase in cost and a loss of performance (duplexer will bring performance The main reason for the loss is that one more device will inevitably bring about insertion loss, and the insertion loss will affect the transmission power of the terminal, thereby affecting the coverage performance of the terminal); 3) Supporting simultaneous transmission of data on multiple frequency bands may introduce intermodulation and harmonic interference, which will affect terminal performance (such as uplink and downlink rates and coverage capabilities). Therefore, compared with the SA architecture, although 5G terminals supporting the NSA architecture will mature earlier and have a faster downlink rate, they are more challenging in design, and the cost of radio frequency devices will be higher, and the performance will be higher. There will be a decline. We make OBD connector with terminal by ourselves,
soldering type and crimping type are both available. Also 12V and 24V
type. OBD1, OB2, J1939, J1708, J1962, etc. Also molded by different
type, straight type or right-angle type. The OBD connector cables used
for Audi, Honda, Toyota, BWM, etc. We have wide range of materials
source , also we can support customers to make a customized one to
replace the original ones. Sae J1708 Connector,Sae J1939 Connector,OBD2 Diagnostic Connectors,Diagnostic Connector,Deutsch Diagnostic Connector ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.etopwireharness.com